Automating Risk Management in Forex Trading: BrokerHiveX 2025 Expert Guide
Summary:Automated forex trading without risk management can easily lead to significant losses. This article, based on expert analysis from BrokerHivex, details key strategies such as drawdown control, position sizing, EA risk management features, and broker selection. Discipline, data, and a compliant platform are the core of building a robust EA system.
Introduction: Why risk management is essential in automated trading
Did you know? According to Investopedia, 90% of retail forex traders lose money due to insufficient risk control. This stark statistic highlights the importance of robust risk management in the age of automation. While expert advisors (EAs) and algorithmic systems offer 24/7 execution and emotion-free trading, they can also amplify losses if there are no control mechanisms.
The paradox of automated trading is that while EAs can execute strategies with pinpoint accuracy, without risk mitigation measures, a single market anomaly or code bug can trigger a catastrophic drawdown. This guide, compiled by the BrokerHiveX expert team, offers practical strategies, real-world examples, and proprietary broker/EA analysis to help you build a compliant, secure, and sustainable automated trading system.
Part 1: Core Risk Indicators Every EA Trader Must Monitor
Infographic: Showcases key risk control components in automated forex trading, such as stop-loss, position control, and asset diversification.
1.1 Drawdown: The invisible killer of accounts
Drawdown measures the extent of an account's loss from peak to trough, and is a core indicator of risk exposure. It is mainly divided into two categories:
Absolute drawdown: the difference between the initial balance and the historical lowest balance;
Relative (Maximum) Drawdown: The largest percentage decline from peak to trough in the account's history.
Calculation example:
Initial capital was $10,000, peaked at $12,000, and then dropped to $10,800
Maximum drawdown = ($12,000 - $10,800) / $12,000 = 10%
Case Study:
Leading EA platform XauBot sets a maximum drawdown limit of 11%. Once this value is reached, trading is automatically suspended to protect capital (XauBot provides evidence).
BrokerHivex recommends: Even for aggressive strategies, the maximum drawdown should not exceed 20%. This meets institutional-level risk control standards and contributes to long-term trading stability.
1.2 Effective Risk-Return Ratio (RR Ratio)
An ideal risk-reward ratio is the foundation of sound trading. The industry generally recommends a minimum of 1:2 (risk $1, target profit $2). However, during the volatile period of 2024, EAs with a 1:3 RR ratio outperformed lower RR strategies in terms of both drawdown control and net profit.
Interactive tool suggestions:
Use BrokerHiveX's "Risk Simulator" tool to simulate the long-term impact of different RR ratios on the account curve.
1.3 Position Control: The First Step in Risk Defense
Position size determines your actual risk on each trade. The "2% Rule" suggests risking no more than 2% of your account balance on each trade.
For example, if your account is $10,000, the risk per order should not exceed $200.
Average Trend Analysis (ATR):
Use the ATR indicator to dynamically adjust lot size to adapt to market fluctuations. For example, if the ATR is 50 points and the planned risk is $200, then:
Lot size = $200 ÷ (50 × pip value)
Common mistakes:
Many traders mistakenly believe that small lots are safe, but ignore the multiplied risks brought about by EA's multiple orders or high leverage.
Part 2: Advanced Risk Control Strategies in EA Trading
2.1 Dynamic Stop-Loss Strategy
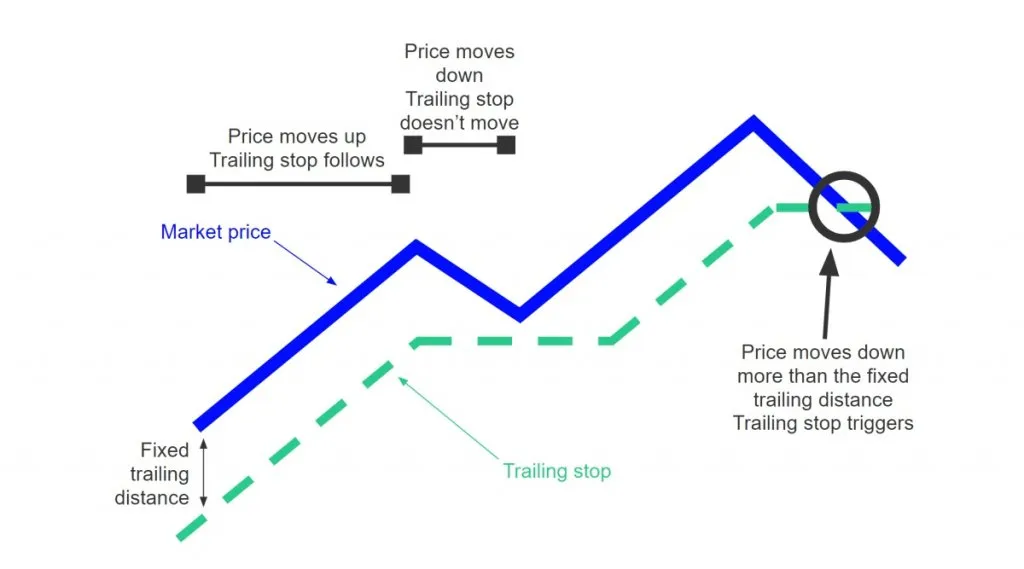
Flowchart: Demonstrates the logic for setting and adjusting stop-loss orders, including fixed, dynamic, and trailing stop-loss settings.
Stop Loss Type:
Fixed stop loss: set below a fixed price at the opening point;
Trailing stop loss: automatically adjusts upwards as the market moves in a favorable direction to lock in profits.
Usage scenarios:
Range-bound market → Fixed stop loss
Trending Market → Trailing Stop
Code Example (Trailing Stop Based on ATR, PineScript):
pinescript copy edit stop_level = close - atr(14) * 2
strategy.exit("ATR Stop", stop=stop_level) Platform comparison:
Pepperstone VPS offers low-latency execution, reducing stop-loss slippage; IC Markets offers stronger slippage control, improving EA execution reliability.
2.2 Multiple drawdown protection mechanisms
Modern EAs (such as FXStabilizer PRO) allow you to set daily or weekly maximum loss limits, for example, automatically suspending trading if daily losses exceed 5% or if there are three consecutive losing trades. This "circuit breaker" mechanism is an effective way to prevent consecutive losses.
Regulatory perspective:
NFA and FCA require EA systems and brokers to have complete risk management documentation, including automatic liquidation records and real-time monitoring capabilities.
2.3 Diversification: More than just currency pairs
Diversification isn't limited to multiple currency pairs. Consider adding gold, indices, or cryptocurrencies to create a portfolio of uncorrelated assets.
Case Study:
A simulated hedge fund portfolio using three uncorrelated EAs (trading EUR/USD, gold, and BTC/USD) achieved a maximum drawdown 30% lower than that of a single instrument (data source: EA Trading Academy).
Note: Excessive decentralization may lead to decreased efficiency and increased complexity.
Part 3: Broker Risk Control Tools You May Have Ignored
3.1 Comparison of Negative Balance Protection Mechanisms
The BrokerHivex regulatory rating system shows that not all platforms offer negative balance protection:
| platform | Negative balance protection | score | Regulatory agencies |
|---|---|---|---|
| FP Markets | have | 9.2/10 | ASIC |
| FXTM | have | 8.8/10 | FCA |
| Octa | Partial support | 8.1/10 | CySEC |
In the simulated flash crash environment, brokers with protection mechanisms successfully prevented user funds from going negative, while some platforms did not have such protection.
3.2 Execution Quality and Slippage Control
ECN vs STP:
ECN platforms (Electronic Communication Network) offer lower spreads and faster execution, making them suitable for news-driven markets.
STP (Straight Through Processing) platforms may experience slippage fluctuations.
Practical function recommendations:
cTrader provides a "maximum slippage" parameter setting, allowing users to define the maximum acceptable slippage value to enhance risk control.
3.3 VPS Selection Recommendations
Latency determines the success or failure of an EA's performance.
BrokerHiveX's actual test shows that:
European users should choose London VPS;
North American traders should choose a New York VPS server.
Top 3 VPS recommendations for 2025:
Beeks Financial Cloud
CNS VPS
ForexVPS.net
Part 4: Regulatory Compliance & Conduct Risk Warning
4.1 NFA/FCA Risk Control Compliance Checklist
If an EA system needs to meet regulatory requirements, it should include:
Automatic liquidation (when the maximum drawdown is reached)
Comprehensively record risk events and parameter changes
Daily/weekly loss limits
Real-time abnormality prompts (such as slippage, delay)
Manual intervention channel (deactivate EA in emergency)
Warning sign: Brokers that do not provide transparent risk control records should be used with caution.
4.2 Behavioral Risk: Can You Just Set Up an EA and Leave It Alone?
"Set it and forget it" is a fatal mistake. Even the most advanced EAs require regular checking and parameter adjustments.
Common psychological misunderstandings:
Traders often manually shut down EA after consecutive losses, which disrupts the system's rhythm.
Best Practices:
Review the EA parameter configuration once a month. You can use the checking tools provided in the BrokerHiveX Expert List or Expert Profile.
Conclusion: Build your personalized risk management system
The success of automated trading relies on a rigorous risk management framework. Here are some recommended steps to implement it:
Set the maximum acceptable drawdown (recommended not to exceed 15%) and have the EA automatically shut down when triggered
Use ATR to dynamically adjust positions and match lot sizes based on market fluctuations
Choose a broker with negative balance protection and transparent risk control logs
Review strategies and backtesting results quarterly and continuously optimize EA parameters
This article is provided by BrokerHiveX , which specializes in broker ratings, regulatory information, and professional trading education. For more of the latest financial news and expert analysis, please visit our website.
References:
⚠️Risk Warning and Disclaimer
BrokerHivex is a financial media platform that displays information from the public internet or user-uploaded content. BrokerHivex does not support any trading platform or instrument. We are not responsible for any trading disputes or losses arising from the use of this information. Please note that the information displayed on the platform may be delayed, and users should independently verify its accuracy.