 BrokerHiveX
BrokerHiveX BrokerHiveX
BrokerHiveX BrokerHiveX
BrokerHiveXSummary:Leverage trading is one of the most powerful—and dangerous—tools in modern financial markets. It allows traders to control the market with capital far smaller than their position size, thereby magnifying both profits and losses. This "amplifier" effect is a double-edged sword: while it can accelerate gains, it can also quickly magnify losses, often leading to the dreaded margin call.
Leveraged trading is one of the most powerful—and dangerous—tools in modern financial markets. It allows traders to control the market with capital far smaller than their position size, magnifying both profits and losses. This "amplifier" effect is a double-edged sword: while it can accelerate gains, it can also quickly magnify losses, often leading to dreaded margin calls. According to the UK's Financial Conduct Authority (FCA), 74% to 89% of retail Contract for Difference (CFD) traders lose money, highlighting the importance of understanding leverage and margin mechanics before trading.
A margin call is more than just a technical event—it can mean the difference between life and death for your account. Effective risk management is crucial to avoiding margin calls and forced liquidations. This guide, powered by BrokerHiveX's authoritative data and regulatory insights, provides you with the knowledge and tools to manage leverage risk, implement a robust stop-loss strategy, and maintain trading discipline. As a trusted source for global broker rankings, regulatory information, and expert market analysis, BrokerHiveX is an indispensable resource for traders and professionals.
Leverage allows traders to control larger positions with relatively less capital (i.e., margin ). The leverage ratio (e.g., 50:1) determines the market exposure per unit of capital. For example, 50:1 leverage means that a $1,000 margin deposit can control a $50,000 position.
Mathematical relationship:
Leverage Ratio = Position Size ÷ Margin
Margin requirement (%) = 1 ÷ leverage ratio × 100
example:
If you want to open a $100,000 position with 50:1 leverage, you will need $2,000 in margin (100,000 ÷ 50 = 2,000). If the market moves 2% against you, your entire margin could be wiped out.
The "amplifier" effect has been widely documented:
“In CFD trading, leverage is a core factor determining both opportunity and risk. This ‘amplifier’ effect is a double-edged sword: it can magnify profits but also accelerate losses.”
—— BrokerHiveX source
For more detailed explanation of leverage mechanisms and regulatory restrictions, please refer to BrokerHiveX’s CFD Leverage Guide .
Margin requirements are set by brokers and monitored by regulators to ensure traders have sufficient capital to cover potential losses. By 2025, major regulators (such as the UK's FCA, the EU's ESMA, and Australia's ASIC) had implemented strict leverage caps for retail traders, typically capping leverage at 30:1 in forex trading.
“Following events such as the Swiss Franc crisis in 2015, ESMA and the FCA began restricting leverage to prevent retail investors from being liquidated due to extreme market volatility.”
—— BrokerHiveX source
These limits are designed to protect retail investors from excessive risk and extreme market volatility. For the latest leverage policies and margin requirements in different regions, please consult the BrokerHiveX regulatory database .
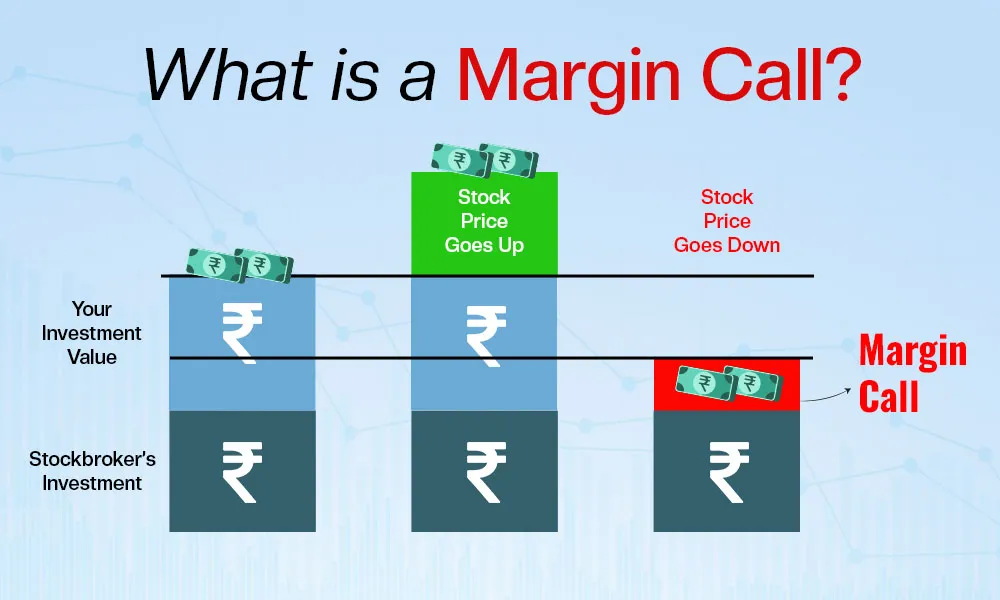
A margin call occurs when your account equity (balance ± profit or loss on open positions) falls below your used margin level. At this point, your available margin is zero, and you cannot open new positions. If losses continue, your broker may force liquidate any positions to prevent your account from going into negative territory.
“When the account equity equals the margin, a margin call is triggered, which means the available margin is zero and new positions cannot be opened.”
—— FP Markets source
Key Stats:
“80% of margin calls occur when leverage exceeds 50:1.”
—— BrokerHiveX source
This shows that there is a direct link between high leverage and margin call risk.
(The following content continues to be translated point by point, including the margin call calculation formula , risk management strategy , stop-loss/position management/leverage selection , trading discipline and psychological management , choosing a compliant broker , measures to deal with margin calls, conclusion , and appendix (glossary, case studies, tools) .)
Margin Call calculation formula:
Margin Level (%) = (Account Equity ÷ Used Margin) × 100
A margin call is triggered when the margin level falls below a threshold set by the broker (usually 100%).
example:
If you have $1,000 in account equity and have used $1,000 in margin, your margin level is 100%. If your equity drops to $900, your margin level becomes 90%, which could trigger a margin call (depending on your broker's policies).
Your broker may notify you of a margin call, but is not always obliged to do so.
"Your broker has the discretion to ask you to increase your account equity. Some firms will try to contact you, but they are not obligated to do so. They can sell any security immediately without regard to your financial and tax obligations."
—— Fidelity source
Ignoring margin calls can result in forced liquidation, often at unfavorable prices. For more details, please see BrokerHiveX's Margin Call Policy and Risk Disclosure .
Stop-loss orders are essential tools for limiting losses and preventing your account from triggering margin calls. A fixed stop-loss sets a predetermined exit point, while a trailing stop-loss automatically adjusts as the market moves in your favor, helping you lock in profits and reduce risk.
“Use stop-loss orders or trailing stops to avoid margin calls. These orders limit your losses and prevent your account value from falling below your maintenance margin level.”
—— BabyPips source
Best Practices:
Set stop-loss based on market volatility (e.g. using the ATR indicator).
Avoid increasing the distance between your stops just to “give the trade more room”.
Use a trailing stop to dynamically protect profits.
For more expert guidance, please refer to BrokerHiveX's expert insights on using stop-loss orders .
Reasonable position sizing ensures that a single trade does not threaten the survival of your account. Position sizing should be calculated based on your risk tolerance (e.g., risk no more than 1-2% of your account equity per trade).
Building a position in batches means opening a small position first, and then gradually increasing the position when the trend is confirmed to be favorable, rather than investing the entire position at one time.
“Buying a position in batches means starting with a small position and gradually increasing it as the price moves in your favor, adjusting your stop-loss. This approach is less risky than going all in at once and is less likely to trigger a margin call.”
—— BabyPips source
Case Study:
A trader with $10,000 in account equity risks 1% ($100) per trade. Instead of opening a $50,000 position all at once, they start with $10,000, gradually adding to their position as profits build, and adjusting their stop-loss to protect their gains. This approach reduces their risk exposure and the likelihood of triggering a margin call.
It is important to choose a leverage that suits your risk tolerance and trading style. Excessive leverage (e.g. >50:1) can significantly increase margin call risk, especially during periods of volatile market conditions.
“The leverage you choose should be based on your risk appetite, trading strategy, and account size. There is no such thing as ‘universal leverage’; there is only the leverage level that works best for you.”
—— BrokerHiveX source
BrokerHiveX data:
80% of margin calls occur when leverage is above 50:1. Most traders recommend using conservative leverage (≤10:1).
Guidance suggestions:
Reduce leverage during periods of high volatility.
Adjust leverage levels regularly as market conditions change.
It is crucial to monitor margin levels and available margin on a daily basis. Set a personal margin threshold that is higher than your broker's minimum requirement and take proactive action when it approaches.
“Effective risk management includes allocating positions appropriately, setting stop-loss orders, and continuously monitoring account margin.”
—— BrokerHiveX source
tool:
Manage actively with BrokerHiveX's real-time quotes and margin calculator.
Maintain sufficient account equity to avoid forced liquidation.
Trading discipline means strictly adhering to trading plans and risk management rules, without being affected by emotions or market noise.
“Trading discipline establishes a protective barrier through stop-loss orders and position management rules. These parameters limit potential losses on a single trade to 1-2% of the total account value, preserving capital for future opportunities.”
—— TradeFundrr source
Statistics:
Disciplined traders limit their losses to 1-2% per trade, while undisciplined traders risk 5-10% and suffer losses 25% higher on average.
Discipline prevents emotional actions, such as revenge trading or excessive use of leverage, which often lead to margin calls.
Maintaining discipline requires mental toughness. Common techniques include:
Keep a trading journal: record trades and emotions, and identify patterns.
Mindfulness practice: Stay in the present moment and avoid impulsive decision-making.
Pre-trade checklist: Confirm that all risk conditions are met before entering the market.
Behavioral finance research shows that managing fear and greed is crucial to avoiding excessive leverage and overtrading. For more behavioral strategies, see BrokerHiveX expert insights .
Regulatory oversight ensures that brokers adhere to margin and leverage rules, thereby protecting traders from unfair practices.
“Following events such as the Swiss Franc crisis in 2015, ESMA and the FCA began restricting leverage to prevent retail investors from being liquidated due to extreme market volatility.”
—— BrokerHiveX source
BrokerHiveX provides verified broker rankings and regulatory status to help you choose a broker with the following characteristics:
Negative balance protection
Margin Call Reminder
Advanced risk management tools
Top brokers typically offer the following features:
Advanced order types: Stop Loss, Trailing Stop, Guaranteed Stop
Real-time margin calls
Built-in margin calculator
For a list of brokers with excellent risk control features, see BrokerHiveX Recommended Brokers .
If you receive a margin call, you can:
Add funds to restore margin levels
Close losing positions to reduce margin usage
“To meet margin calls, traders have two options: add funds to their accounts or close some of their positions. If they fail to meet margin requirements, their positions may be forcibly closed by their broker.”
—— FBS source
Ignoring margin calls can result in forced liquidation, often without prior notice. Communicate with your broker promptly to understand your options.
After a margin call, you should:
Review and adjust trading strategies to prevent recurrence
Re-evaluate leverage and position sizing
Leverage BrokerHiveX’s educational resources and expert analysis to continuously improve
For more learning resources, please refer to BrokerHiveX educational resources .
Leveraged trading offers tremendous opportunities, but also carries significant risks. Mastering risk management is crucial to avoiding margin calls and protecting capital. Key points include:
Understanding leverage and margin mechanisms
Understanding Margin Call Triggers and Consequences
Use robust risk management tools (stop-loss, position control, conservative leverage)
Maintain trading discipline and mental toughness
Choose a regulated broker and use their risk management tools
Leverage BrokerHiveX's authoritative data and resources to help you make informed broker choices and manage risk. For more insights, access global forex broker rankings , regulatory databases , and financial news .
| the term | definition |
|---|---|
| Margin Call | A notification from a broker requesting additional funds when the account equity falls to the used margin level. |
| lever | Use borrowed funds to increase the size of your trading positions. |
| Stop Loss | An order that automatically closes a position at a preset loss threshold. |
| Margin Requirements | The minimum funds required to open/maintain a leveraged position. |
| Available Margin | Account equity that can be used to open new positions. |
For a hands-on tool to calculate your margin call risk, use the BrokerHiveX Margin Calculator .
Example 1: A trader opens a $100,000 position using 100:1 leverage on a $1,000 account. A 1% adverse movement wipes out the margin, triggering a margin call and resulting in a forced liquidation.
Case 2: Another trader used 10:1 leverage, set a 2% stop-loss risk, and entered positions in batches. Even in volatile markets, their account remained above their margin requirements, successfully avoiding margin calls.
This guide is brought to you by BrokerHiveX, your definitive source for global broker rankings, regulatory data, and expert market insights. For more information, visit BrokerHiveX .
BrokerHivex is a financial media platform that displays information sourced from the public internet or uploaded by users. BrokerHivex does not endorse any trading platform or instrument. We are not responsible for any trading disputes or losses arising from the use of this information. Please note that the information displayed on the platform may be delayed, and users should independently verify its accuracy.